Tailbones

by Jon Burch Photography
Buy the Original Photograph
Price
$275
Dimensions
24.000 x 16.000 inches
This original photograph is currently for sale. At the present time, originals are not offered for sale through the Jon Burch Photography - Website secure checkout system. Please contact the artist directly to inquire about purchasing this original.
Click here to contact the artist.
Title
Tailbones
Artist
Jon Burch Photography
Medium
Photograph - Digital Capture/vintage Film
Description
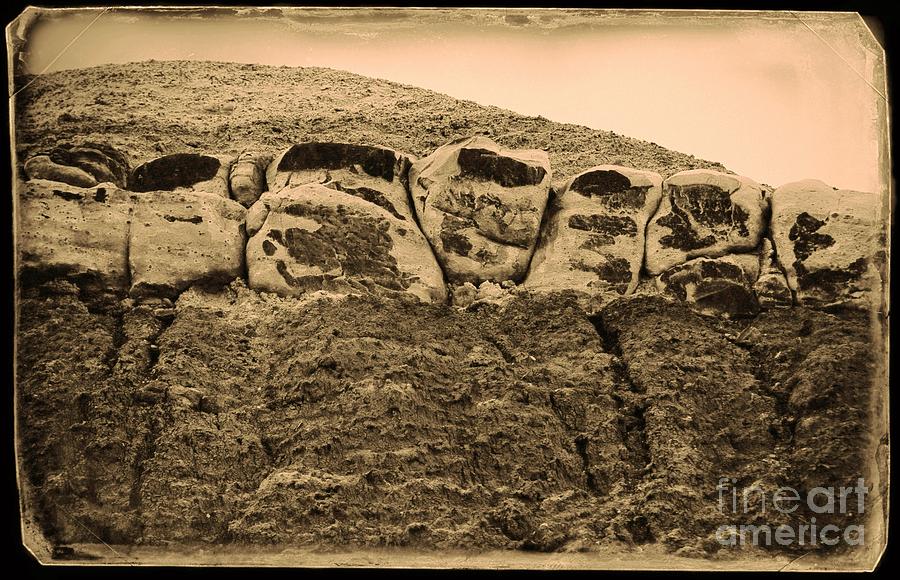
The quarry on Dinosaur Hill near Fruita, Colorado is where a 70 foot long Apatosaurus was excavated by Elmer Riggs and his crew in 1901. Riggs was an Assistant Curator of Paleontology at the Field museum in Chicago. Apatosaurus is a genus that includes the popular synonym Brontosaurus, a sauropod dinosaur that lived from about 154 to 150 million years ago, during the Jurassic Period within the 600-foot-thick Morrison Formation. It was one of the largest land animals known to have ever existed, with an average length of 75 feet and a mass of at least 16 metric tons. This skeleton is now displayed at the Chicago Field Museum of Natural History.
A tunnel was blasted into the hillside where many bones of the dinosaur's skeleton were recovered. The tunnel was reopened in 1991 by a team of paleontologists who found an additional set of tail bones called chevrons.
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that occurred 201 to 145 Million years ago marking the end of the previous Triassic period to the beginning of the later Cretaceous. It is named after the Jura Mountains within the European Alps, where period specific limestone strata was first identified.
The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era, also known as the Age of Reptiles the start of which is marked by the major Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. Another extinction event, the Late Piensbachian/Early Toarcian event, occurred in the Early Jurassic, and a third extinction event, the Late Tithonian event, occurred at the end of the Jurassic; however neither of these two events rank among the 'Big Five' mass extinction.
By the beginning of the Jurassic, the supercontinent Pangaea had begun rifting into two landmasses, Laurasia to the north and Gondwana to the south. This created more coastlines and shifted the continental climate from dry to humid, and many of the arid deserts of the Triassic were replaced by lush rainforests. On land, the fauna transitioned from the Triassic fauna, dominated by both dinosauromorph and crocodilomorph archosaurs, to one dominated by dinosaurs. The first birds also appeared during the Jurassic, having evolved from a branch of theropod dinosaurs. Other major events include the appearance of the earliest lizards, and the evolution of therian mammals, including primitive placentals. Crocodylians made the transition from a terrestrial to an aquatic mode of life. The oceans were inhabited by marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs, while pterosaurs were the dominant flying vertebrates. It was during these times that these hills were formed.
Image copyright 2013 Jon Burch Photography
Uploaded
August 24th, 2013
Embed
Share